 |
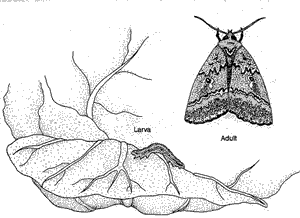
Light green worm with long yellowish stripes on back (not to be confused with the worm of diamond-backed moth or imported cabbage worm which are similar). Its distinctive characteristic is that it loops as it walks. Adult: brownish night-flying moth with a silvery spot in the middle of each forewing; 1 1/2-inch wingspan. Eggs: Greenish white, round.
Vulnerable Plants - Lima beans, broccoli, brussel sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, Chinese cabbage, collards, kale, kohlrabi, lettuce, radishes, rutabagas, turnips, parsley. They will also attack geraniums and nasturtiums.
Emergence Times - Have several broods per year. Pupae over-winter by attaching themselves to leaves, except in the extreme north, where the moths migrate south during the cold months.
Symptoms
Small to large ragged holes in leaves; later in season the worms bore into developing heads of cabbage family crops. Seedlings can be wiped out
Early Warning Trick Using Trap Crops - Celery can be used as a trap crop to spot early infestations of cabbage looper. Locate it within 10 to 15 feet of the crop threatened by the cabbage looper. Amaranth is attacked by cabbage loopers and is another option for a trap crop.

