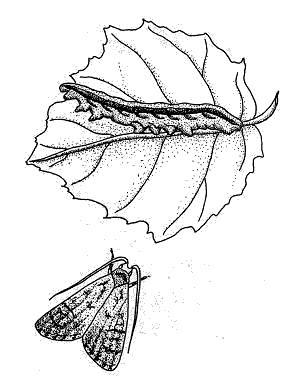
 |
The Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) is the caterpillar of a gray mottled moth. It is about 1 and 1/2 to 1 3/4 inches long and has a somewhat hairy body. They are somewhat larger than the sod webworm. It is usually brown, but may be green or black, and has a black head. Three yellowish white hairlines stretch down its back from head to tail. You'll find a dark stripe along either side, and below that a wavy yellow line splotched with red. A white V or Y marks its head.
Only one generation occurs each year in the North. The eggs are covered with hair and are laid in clusters of 50 to 150. Young white larvae hang from threads or curl up in leaves. Fall armyworms are found throughout most of North America, except in the far north.
The adult is a gray, mottled night flying moth with a 2 inch wingspan. The adults migrate south for the winter.
Emergent Times - In the spring, swarms of moths fly North and lay eggs, and the caterpillars begin their devastation in the fall.
Nature's Armyworm Control System
If your yard has good diversity of plants, you feed songbirds, and you don't use any broad spectrum insecticides the following beneficial insects and songbirds love to eat aphids and if in sufficient numbers will keep armyworms under control.
Beneficial insect predators - Assassin Bugs, Bigeyed Bugs, Ground or Tiger Beetles,Rove Beetles, Spiders, and Tachinid Flies eat armyworms for lunch.
Songbird predators - Robins and Starlings love armyworms.
If you don't have this army of predators on your property, the rest of this file will help you deal with your armyworm problem.

